Gold continues to hit new highs. How to invest in gold in the crypto market?
Author: Frank, PANews
As Bitcoin encounters a "value winter", real-world gold is recasting the iron curtain of value on the blockchain.
Recently, the volatility of the crypto market has become increasingly uncertain with the changes in the international financial market, and the price trends of mainstream crypto assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and SOL have also fallen into a slump. The market's enthusiasm for crypto trading seems to be moving from optimism to a bearish state. In sharp contrast, the international gold price has been rising all the way to over $3,240 per ounce, constantly setting new historical highs, and the price has once again verified that gold is a safe-haven asset.
In the crypto market, the market value of assets linked to gold has also been rising. On April 11, the market value of tokenized gold assets exceeded US$2 billion. From the perspective of risk hedging, gold-related crypto assets seem to be becoming a new high-quality option. PANews takes stock of the current exposure of mainstream gold-related transactions in the crypto market.
The exposure to gold-related transactions in the crypto market is currently divided into tokenized gold, such as TetherGold (XAUT) or PAXGold (PAXG), which are essentially digital certificates of ownership of physical gold. And derivative transactions using these tokenized gold to trade with stablecoins. For example, XAUT or PAXG spot trading pairs or contract trading pairs provided by exchanges. In addition, some online precious metals traders support cryptocurrencies as payment methods when trading physical gold. These gold participation methods have deviations in risk appetite, funding flexibility, etc.
XAUT and PAXG: Leading Projects in Tokenized Gold
TetherGold (XAUT) and PAXGold (PAXG) are the two largest varieties in the tokenized gold market. XAUT is issued by Tether, the issuer of USDT. 1XAUT corresponds to the ownership of 1 troy ounce of gold on a specific LBMA (London Bullion Market Association)-approved "good delivery" gold bar. Gold is allocated in designated quantities, and holders can query the unique serial number, purity, and weight of the gold bar associated with their address through the official website. Tether claims that its reserves 100% support the issued tokens, and XAUT is partially supported by the gold in the reserves. As of April 12, the total support of XAUT is 7,667.7 kilograms of gold, distributed on 644 gold bars, and the market value of XAUT tokens is approximately US$797 million.
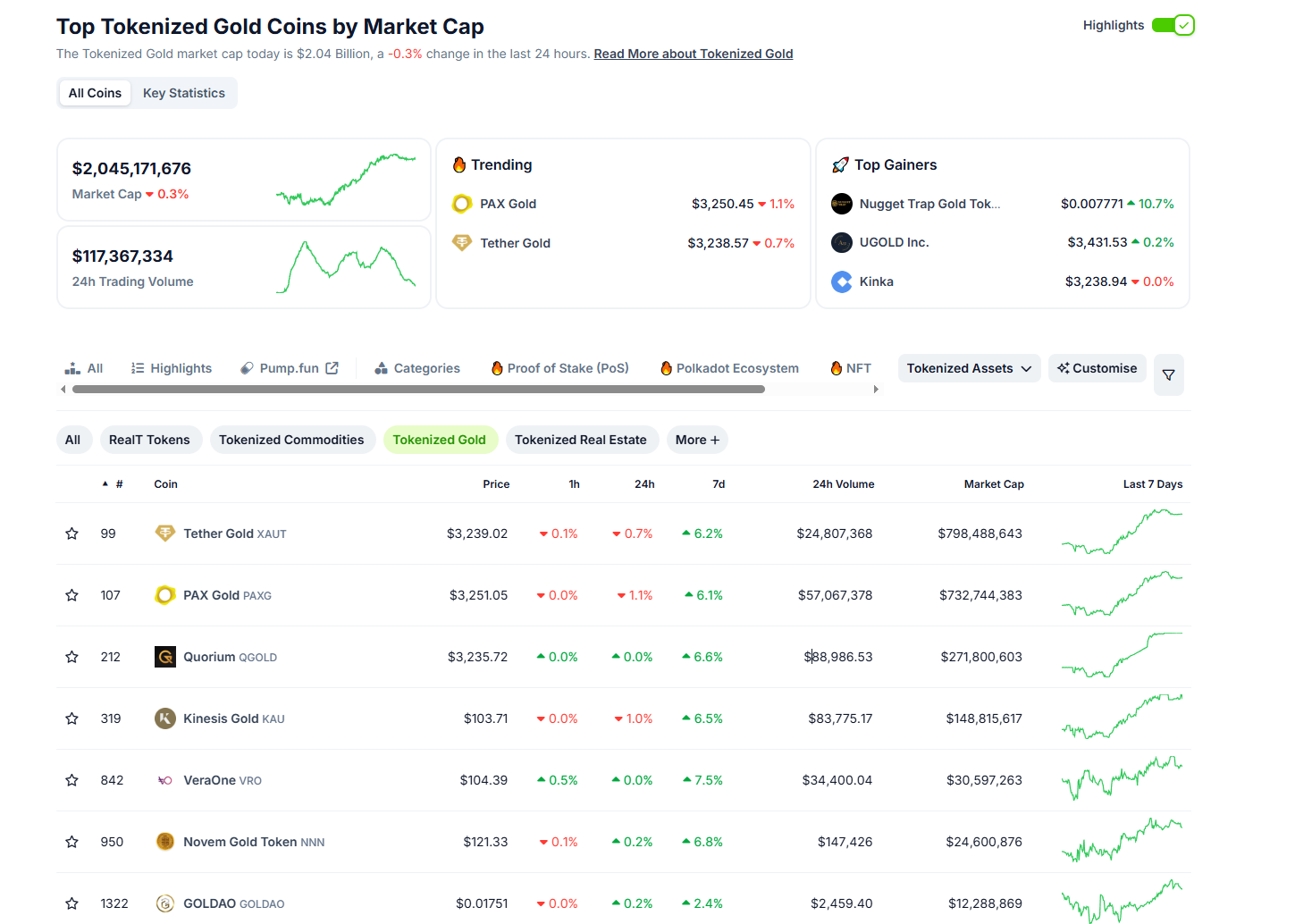 The issuer of PAXG is Paxos Trust Company, a trust company and custodian regulated by the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS). PAXG is also the ownership of 1 troy ounce of London Good Delivery gold bar for each token. A third-party auditing company will issue a report on the monthly issuance of PAXG. As of February 28, the report shows that the company holds 209,160 ounces of gold (about 5,929 kilograms).
The issuer of PAXG is Paxos Trust Company, a trust company and custodian regulated by the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS). PAXG is also the ownership of 1 troy ounce of London Good Delivery gold bar for each token. A third-party auditing company will issue a report on the monthly issuance of PAXG. As of February 28, the report shows that the company holds 209,160 ounces of gold (about 5,929 kilograms).
Compared to traditional gold ETFs or futures, XAUT and PAXG’s tokenized gold have no custody fees and have a smaller minimum purchase amount.
PAXG has a different fee structure than XAUT. Creating or destroying PAXG directly through the Paxos platform incurs a tiered fee based on transaction volume, and on-chain transfers are charged a 0.02% Paxos fee. In contrast, XAUT claims to have no custody fees, but charges a 0.25% fee on direct purchases/redemptions. This means that for small users, trading PAXG on a secondary exchange may be more cost-effective than operating directly through the Paxos platform to avoid creation or destruction fees. Frequent on-chain transfers will incur additional costs for PAXG.
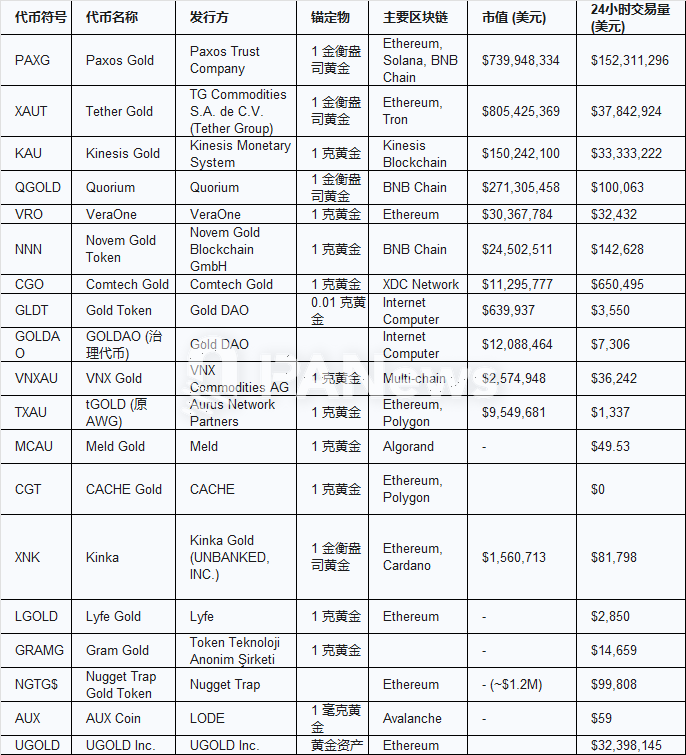
Kinesis, the self-operated mint, and Quorium, the gold mining model
In addition, there are other tokenized gold products with a market value of more than 100 million, including Quorium (QGLOD) and KinesisGold (KAU). QGLOD's business model is relatively special. The gold it holds is essentially a gold mine reserve rather than spot gold. In addition, although the project claims to have regular reports on gold reserves, PANews found that these web pages can no longer be opened. Therefore, it is impossible to understand the reserve situation of QGLOD. The information is vague and contradictory, and lacks key details that are independently verified by a third party. In particular, the concept of "undeveloped reserves", how to provide stable support for liquidity tokens, and how to conduct audits and valuations are all unresolved issues, which brings great uncertainty and risks to investors.
In addition, QGOLD's market data presents some warning signs. Its market capitalization (about $270 million) is relatively high, but its daily trading volume is abnormally low (about $100,000) and concentrated in a few less well-known exchanges. This serious mismatch between market capitalization and trading volume and exchange liquidity, coupled with a lack of transparency, makes QGOLD's security seem unconvincing.
KinesisGold is priced differently from PAXG or XAUT, with each token representing 1 gram of gold. Its core differentiation lies in its unique revenue sharing model. Unlike tokens such as PAXG and XAUT that only track gold prices, KAU returns part of the platform's transaction fees to holders in the form of gold (KAU). However, this income is not fixed or risk-free, and its size depends directly on the overall transaction volume and fee income of the Kinesis platform. In addition, Kinesis has also launched a corresponding virtual card, and users can directly use KAU for daily consumption, which is also different from KAU. In terms of transparency, Kinesis chooses to audit every six months and supports physical delivery of every 100 grams. According to Kinesis' official information, Kinesis operates a 5,600-square-meter mint and refinery, KinesisMint, which produces high-quality gold and silver ingot products.
In terms of market circulation, XAUT and PAXG are still the two most liquid tokenized golds, and can be traded on many mainstream centralized exchanges and DEXs. KAU can be traded on its own KinesisExchange platform as well as centralized exchanges such as BitMart and Emirex, but its liquidity is slightly insufficient.
There is a lot of exposure to spot delivery payments, and gold tokens are difficult to break the DeFi dimension wall
In addition to tokenized gold, many traditional precious metals traders also support payment in cryptocurrencies. This gold exposure is mainly applicable to spot trading, and cryptocurrencies are only used as a payment method, rather than a fundamental change in the business model. In addition, this type of trading method usually requires a higher threshold for one-time investment, and many platforms trade products such as gold coins or gold medals. In addition to the value of gold itself, users may also need to have product identification and premium identification capabilities.
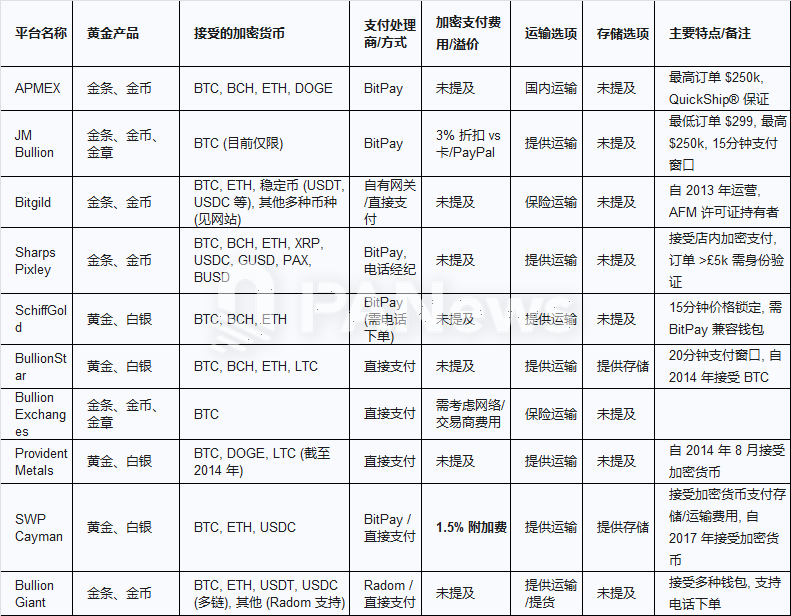
In addition to trading tokenized gold such as PAXG or XAUT, there are some centralized exchanges that offer different types of gold trading. For example, Bybit offers gold contracts for difference (CFDs), which allow traders to speculate on price changes of assets (such as gold) without actually owning the asset. This type of trading is similar to index contract trading in the financial market, that is, users only follow the trend of gold prices to open contract orders, but ultimately cannot deliver spot gold. Among the mainstream centralized exchanges, it seems that only Bybit offers similar products, but many traditional XAU/USD CFD platforms now also accept cryptocurrency deposits, such as FP Markets, Fusion Markets, easyMarkets, etc. This trading method is more suitable for professional traders who are familiar with gold and foreign exchange transactions rather than cryptocurrency investors.
In addition, although gold tokens have the attributes of RWA, the adoption of such products on mainstream DeFi lending platforms seems limited. In addition to PAXG, which can earn staking income through Morpho, leading protocols such as Aave and Compound do not accept gold tokens as native collateral. This may be due to several factors: first, there may be challenges in reliable and decentralized gold price oracles, which are crucial for liquidation mechanisms; second, potential regulatory uncertainties; third, the market demand for gold tokens as collateral may be relatively low compared to ETH or mainstream stablecoins.
In general, the most mainstream way for the crypto market to participate in gold asset exposure may still be to hold mainstream, highly liquid gold tokens such as PAXG or XAUT. In addition, although there are many similar tokenized gold products, due to the identification of issuers and transparency, users may have to consider the security issues involved when choosing these assets. Although buying physical gold directly through traditional precious metal dealers who accept cryptocurrency payments provides the most direct ownership, it is also accompanied by higher thresholds and potential product premium issues. In the field of DeFi, the participation methods of gold assets are still relatively limited, which may also be the difficulty of the deep integration of most RWA assets with on-chain finance.
When Bitcoin holders in the downward cycle begin to turn their attention to real gold, this is not only a footnote to the maturity of the crypto market, but also a value counterattack launched by digital gold against the real world.
You May Also Like

Canary Capital files for spot MOG ETF as XRP fund hits Nasdaq

Bitcoin “Arguably Undervalued,” Says Analytics Firm: Here’s Why