Ethereum Activity Hits Record High While Gas Fees Remain Near All-time lows
TLDR
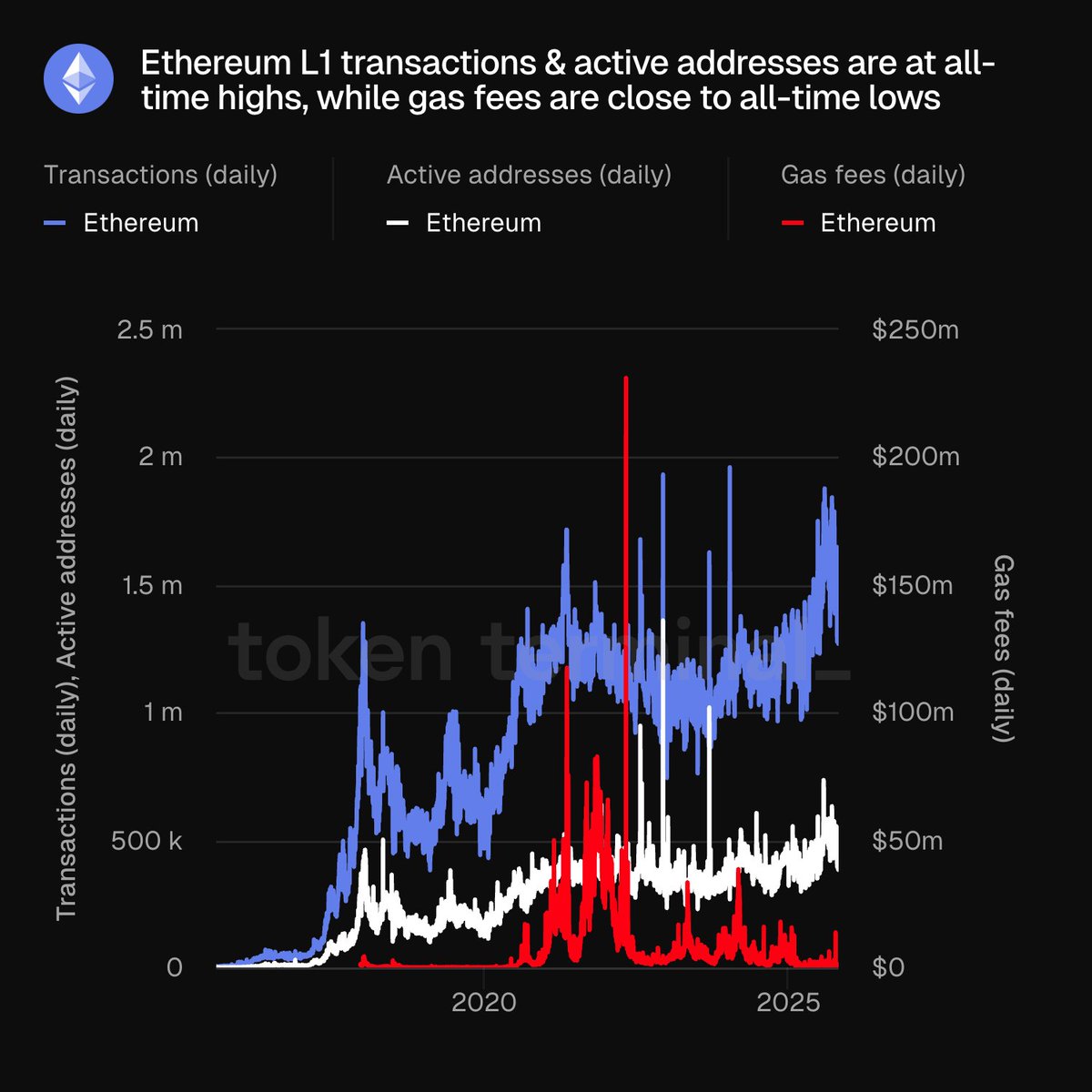
- Ethereum transactions and active addresses are at all-time highs in October 2025.
- Average Ethereum gas fees remain low despite record mainnet usage.
- Layer-2 networks like Arbitrum and Optimism help keep Ethereum fees low.
- Rollups and EIP-4844 upgrades are improving Ethereum’s efficiency at scale.
Ethereum has recorded its highest-ever on-chain activity, with transaction volumes and unique active addresses reaching new peaks. According to Token Terminal, these records were set without the typical rise in gas fees. Despite the surge in demand, transaction costs on Ethereum have remained close to historic lows. This development has captured attention across the blockchain industry, especially among users, developers, and long-term participants.
Record Activity on Ethereum Mainnet
Recent data from Token Terminal shows that ETH Layer 1 (L1) has reached record numbers in daily transactions and unique active addresses. The network is currently processing millions of transactions each day, surpassing past monthly averages.
Analytics platforms confirm that usage across decentralized finance (DeFi), NFT platforms, and other on-chain applications is increasing. This activity is helping to push Ethereum usage to its highest levels to date. Developers have also reported that the network is handling the increased load without notable congestion issues.
Much of this growth is tied to higher engagement with decentralized applications and improved user experiences. Ethereum’s throughput on the mainnet has expanded in both volume and scale, further showing the rising demand for on-chain services. This activity suggests that more users are interacting directly with Ethereum or through connected applications.
Gas Fees Remain Low Despite Heavy Network Usage
Gas fees have remained low even as activity on Ethereum has climbed to new highs. Historically, any rise in transactions on Ethereum would lead to higher gas costs due to congestion. This time, however, that pattern has not occurred.
Ethereum’s current average gas fees are near historic lows. Market observers suggest this shift is due to the growing use of Layer-2 (L2) networks such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base. These L2 chains bundle transactions off-chain and settle them on the mainnet in batches.
By offloading traffic from the base layer, L2s reduce the number of direct transactions on Ethereum L1. This system allows for high throughput while keeping user transaction fees lower. Developers also note that new smart contract designs and protocol upgrades are improving how efficiently Ethereum handles load.
Technology Upgrades Help Support High Activity
The Ethereum network has benefited from a series of infrastructure upgrades that improve its ability to scale. One such upgrade, known as EIP-4844 or proto-danksharding, is expected to further reduce costs and boost data availability on L2 networks.
Since Ethereum transitioned from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, it has become more energy-efficient and structurally flexible. These changes have laid the foundation for handling increased activity without slowing the network or raising fees.
Rollups, which are a key part of ETH roadmap, are being adopted at a growing pace. These scaling solutions process transactions efficiently and help maintain a balanced load on the mainnet. Together with protocol upgrades, they are creating better conditions for both users and developers.
Outlook for Ethereum Network Scalability
Maintaining strong performance while keeping transaction costs low will be a key challenge going forward. ETH developers continue to focus on expanding its capacity while protecting decentralization and security.
The rise in Layer-2 adoption is expected to continue, which may help Ethereum scale more sustainably. As user activity increases across Web3 services, Ethereum will need to keep pace with demand without returning to high gas fee conditions.
For now, Ethereum’s infrastructure appears to be handling the increased pressure well. If these trends continue, Ethereum could remain a central hub for blockchain activity without the high transaction costs that once limited its usability.
The post Ethereum Activity Hits Record High While Gas Fees Remain Near All-time lows appeared first on CoinCentral.
You May Also Like

Why Is Crypto Down Today? – October 30, 2025

The UFC collaboration project, FIGHT tokens, raised $183 million in its public offering, exceeding its target by more than 100 times.
